An evidence-based examination of how technology impacts mental health, exploring both benefits and drawbacks of social media, screen time, and digital wellness tools.
Published: June 2024 10 min read

The evolving relationship between technology and mental health (Source: Appinventiv)
Introduction
We live in an interconnected world in which technology and our mental health are inextricably linked. Whether we’re perpetually connected with our smartphones, our lives being documented on social media or the impact it has had on the way we interact with ourselves, technology has rapidly altered the way we engage with the world. This transition also presents us with enormous opportunities — but also with enormous challenges — to our mental health.
The increasing rates of mental health disorders among young people have been labeled a national crisis. Though this is frequently attributed to something such as the COVID-19 pandemic or poverty, many experts also single out social media as a leading cause of teenagers’ struggles with mental health. 48 percent of teens say social media has a mostly negative effect on people their age, up from 32 percent in 2022, according to recent Pew Research (Getty Images/Andrew Burton) File photo of young people on the internet.
This blog post is the first in a series that will explore the paradoxical relationship between technology and mental health: While technology brings hope, it also brings demons. By understanding how this is a double-edged sword, we can train ourselves to secure the benefits and diminish the harms.
The Digital Mental Health Revolution

The new frontier in health tech: Mental and brain health care Technology has opened up a new frontier in mental health.Providers, with help from tech developers, are creating new ways to tailor and optimize treatment for a variety of conditions. Mobile devices, including smartphones and tablets, are now providing the public, health care providers and researchers with access to new tools to get help, track progress and gain insights into mental wellbeing.
Key Statistics:
- The Global Mental Health Apps Market was valued at USD 5.2 Billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 23.8 Billion by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 16.9%
- Major app stores now offer over 10,000 mental health apps.
- Some 86% of therapy clients say that a teletherapy session is just as effective, if not more so, than an in-person one.
- Approximately 70% of people feel that they are comfortable in seeking mental health help from a Chatbot.
Source: Market.us Technology in Mental Health Statistics
Expanding Access to Mental Health Services
One of the most significant advantages of technology in mental health is how it removes barriers to care. Digital solutions offer accessibility that traditional services cannot match:

Digital mental health tools are revolutionizing mental health care (Source: Mobisoft Infotech)
- Teletherapy and Online Counseling: Approximately 76% of psychologists shifted to teletherapy during the COVID-19 pandemic. Research indicates that 91% of teletherapy clients express satisfaction with the service.
- Mobile Mental Health Apps: Apps like Calm (more than 100 million downloads) and Headspace (more than 65 million downloads) provide meditation, stress and mental wellness offerings.
- Support in times of crisis: Sometimes a crisis goes on currently, and technology can help attend to it at once, as through online crisis lines that are available 24/7.
- Reduced Stigma: Digital interventions allow people to seek help privately, potentially reducing the stigma associated with mental health treatment.
Innovation in Treatment Methods
Technology is transforming treatment approaches with innovative solutions:
- Virtual Reality Therapy: VR exposure therapy demonstrated success rates of 52% in the treatment of social anxiety disorder, and 90% improvement with specific phobias.
- Artificial Intelligence: A.I. algorithms can predict psychosis with 93 percent accuracy and offer treatment suggestions.
- Wearables and Biofeedback: Tools that capture biometric signals support people in recognizing and controlling their stress reactions in the moment.
- Digital Therapeutics: Evidence-based treatment mediated by software is an emerging branch of medicine that is gaining momentum in disease categories such as
The Dark Side: Technology’s Mental Health Challenges
Despite its benefits, technology—particularly social media and excessive screen time—has been linked to significant mental health concerns.
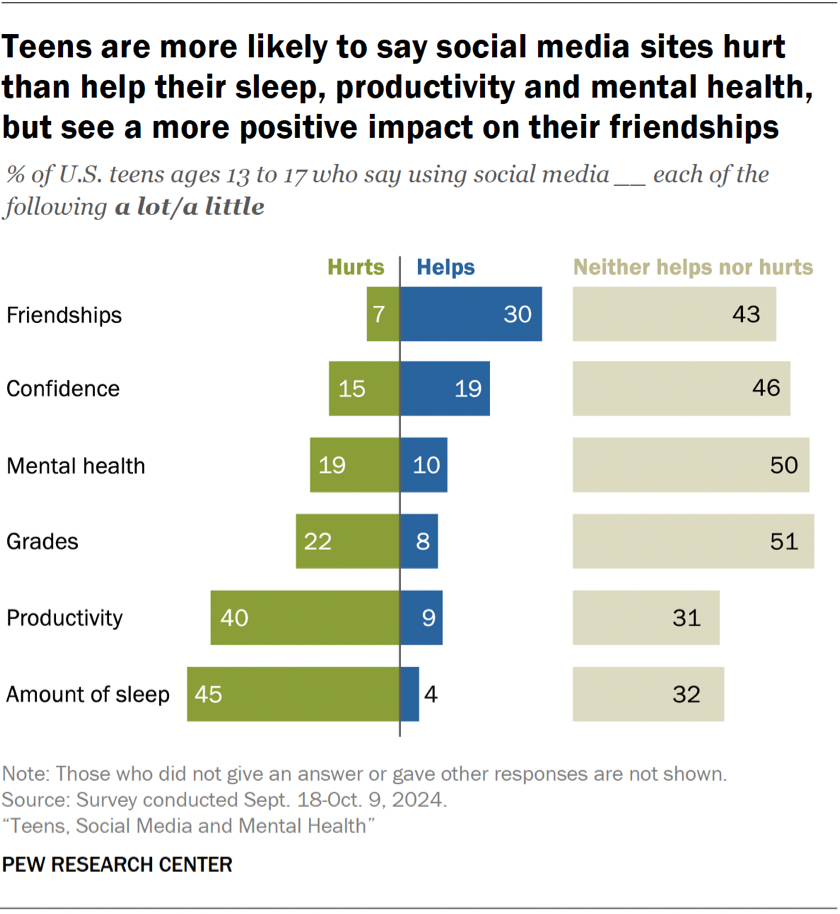
Teens report social media hurts more than helps their sleep, productivity and mental health (Source: Pew Research Center)
Social Media and Mental Health
Social media platforms can significantly impact psychological wellbeing:
“Social media has a reinforcing nature. Using it activates the brain’s reward center by releasing dopamine, a ‘feel-good chemical’ linked to pleasurable activities such as sex, food, and social interaction. The platforms are designed to be addictive and are associated with anxiety, depression, and even physical ailments.”— McLean Hospital
Research findings highlight concerning trends:
- Forty-eight percent of teenagers say that social media channels have a more negative than positive impact on people their age, compared with 32 percent in 2022
- Girls are more likely than boys to say social media hurts their mental health (25 percent vs. 14 percent)
- 45 percent of teens report spending too much time on social media, compared to 36 percent in 2022
- As reported in a systematic review, social media usage is related to a higher risk of depression, anxiety, and psychological well-being problems
The Comparison Trap and FOMO
Social media creates unique psychological challenges:
- Curated Reality: Apps present cherry-picked representations of people’s lives, causing comparison of a less-than-reality self acquaintance.
- FOMO (Fear of Missing Out): Anxiety and a sense of not measuring up generated by your continuous exposure to your peers’ activities.
- Validation Seeking: This continual thirsting for likes and comments can confuse your brain about what true validation is.
- Cyberbullying: Over the past several years, cyberbullying has been held as a leading cause towards depression, anxiety, and in some cases, suicidal thoughts.

Social media mental health statistics infographic (Source: Priory Group)
Screen Time and Sleep Disruption
Excessive screen time has physiological effects that impact mental health:
- A British study published last year linked social media to reduced, interrupted and delayed sleep, which is associated with a greater risk of depression, anxiety and poor performance at school.
- 45% of teens say social media adds unnecessary stress to their lives and makes them overwhelmed, according to a Pew Research study released 12 September 43% of teens say social media distracts them from people they’re with 42% of teens report that social media hurts the amount of sleep they get 40% of teens say social media gives them a less accurate picture of how their friends are doing 35% of teens say social media is a less accurate representation of who they are 31% of teens report that social media makes them feel worse about their personal life 28% of teens say that they feel like they are always missing out on what their friends are doing 27% of teens say social media makes them feel less lonely 26% of teens say social media makes makes them feel better about their personal life 25% of teens say social media helps them understand that a majority of the people they know are also sad sometimes 25% of teens report that social media helps them feel as though they have people who support them through tough times 24% of teens say it makes them feel less depressed
- The blue on-screen light can suppress the production of melatonin, interfering with natural sleep rhythms.
- Low-quality sleep is also highly associated with higher anxiety and depression and decreased cognition.
Gender and Demographic Differences
Research reveals significant disparities in how technology and social media affect different demographic groups:
Gender Differences
Teen girls generally report more negative experiences with technology and social media:
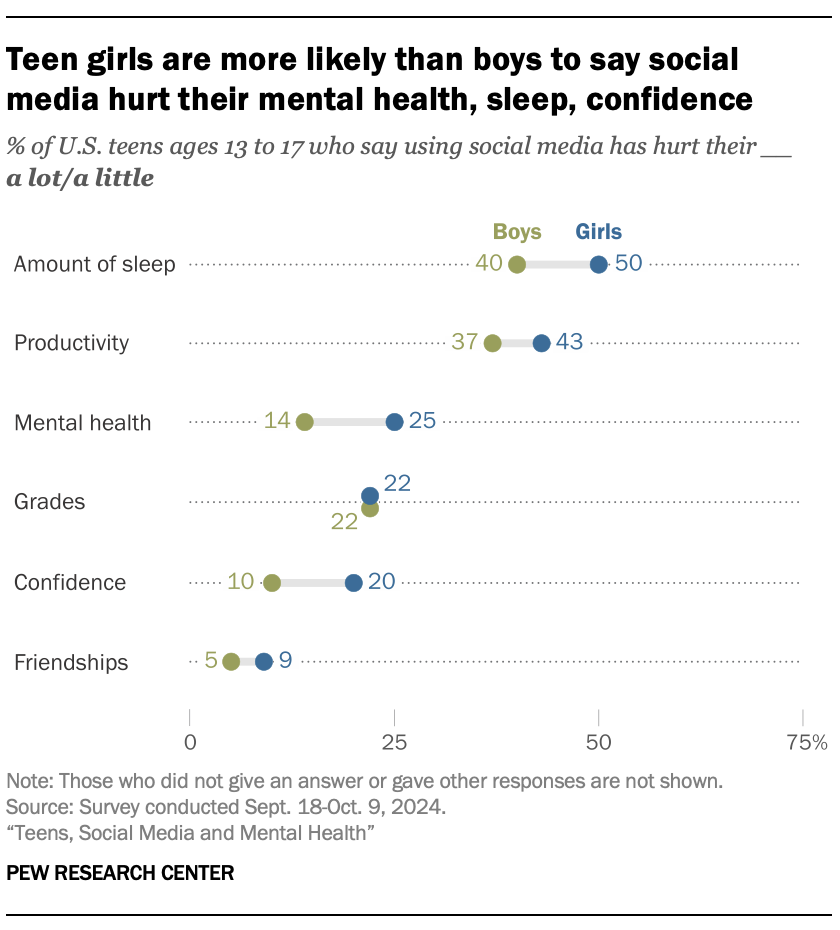
Teen girls are more likely than boys to say social media hurts their mental health, sleep, and confidence (Source: Pew Research Center)
- 25% of teen girls say social media hurts their mental health compared to 14% of boys
- Teen girls are more likely to say social media makes them feel overwhelmed by drama (45% vs. 34% for boys)
- Girls more often report social media creates pressure to post popular content (36% vs. 26%)
- However, girls also report more positive aspects, such as feeling supported (57% vs. 45%) and having a place to show creativity (68% vs. 58%)
Racial and Ethnic Differences

The impacts of technology on mental health vary among racial and ethnic groups:
- Black teens (26%) are more likely than White (12%) or Hispanic (15%) teens to say social media makes them feel like they have a lot of support through tough times
- Black teens (31%) are more likely than White teens (18%) to say social media gives them a place to be creative
- Black teens (49%) are more likely to use social media for mental health information compared to Hispanic (35%) and White (30%) teens
Finding Balance: Digital Wellness Strategies
The key to healthy technology use is finding balance. Here are evidence-based strategies for maintaining digital wellness:
Benefits of Technology
- Increased access to mental health resources
- Connections with supportive communities
- Tools for monitoring and managing mental health
- Reduced stigma through anonymity
- Convenience and lower costs compared to traditional care
Risks of Technology
- Social comparison and FOMO
- Sleep disruption from screen time
- Cyberbullying and online harassment
- Addiction and compulsive use
- Privacy concerns with mental health data
Self-Monitoring Strategies
Evidence suggests self-awareness can reduce negative impacts of technology:
- Track Usage: Monitor screen time and app usage with built-in tools on smartphones
- Conduct Self-Experiments: Rate emotions before and after using social media to identify patterns
- Set Boundaries: Create tech-free times and spaces, especially before bedtime
- Practice Mindful Consumption: Be intentional about what content you consume and how it makes you feel
“A 2018 University of Pennsylvania study found that limiting social media use to 10 minutes per platform per day significantly reduced loneliness and depression over three weeks compared to a control group.”
Family Strategies
Parents can help children develop healthy technology habits:

Types of technology in the mental health space (Source: Aloa)
- Model Healthy Behavior: Children learn from their parents’ technology habits
- Create Family Technology Plans: Set clear rules about when and how technology is used
- Encourage Open Communication: Discuss online experiences and concerns without judgment
- Promote Offline Activities: Balance screen time with physical activity, face-to-face social interaction, and nature exposure
Conclusion: Embracing Technology Mindfully
Technology’s relationship with mental health is indeed a double-edged sword. Digital tools offer unprecedented access to mental health resources and innovative treatments, yet social media and excessive screen time present genuine psychological risks.
The evidence suggests we shouldn’t demonize or idolize technology—rather, we should approach it mindfully. By understanding both its benefits and risks, we can make informed choices about how we integrate technology into our lives and mental health practices.
As digital innovations continue to evolve, so too should our approach to using them. The future of mental health technology looks promising, with increasingly personalized, accessible, and effective tools being developed. Yet the responsibility remains with each of us to use these tools intentionally, setting boundaries that protect our wellbeing while embracing the genuine benefits technology can offer.
By adopting a balanced approach to technology use, we can harness its potential to enhance our mental health while mitigating its risks—transforming what could be a digital burden into a powerful tool for psychological wellness.
References
- Pew Research Center. (2025). “Teens, Social Media and Mental Health.” https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2025/04/22/teens-social-media-and-mental-health/
- National Institute of Mental Health. “Technology and the Future of Mental Health Treatment.” https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/technology-and-the-future-of-mental-health-treatment
- McLean Hospital. (2022). “Here’s How Social Media Affects Your Mental Health.” https://www.mcleanhospital.org/essential/it-or-not-social-medias-affecting-your-mental-health
- Market.us. (2023). “Technology in Mental Health Statistics and Facts.” https://media.market.us/technology-in-mental-health-statistics/
- Nature. (2023). “Digital transformation of mental health services.” https://www.nature.com/articles/s44184-023-00033-y
You can also visit our Other blogs here: luxira.in



